- Markets
- Products
- Services
- News
- Tools & Resources
- About Nexans
- Search
- Contact us
- Compare
- Sign in
Scarlet project - Superconductivity to accelerate the energy transition
Superconducting Cables for Europe’s Clean Energy Future is the ambition of the European project Scarlet, gathering 15 partners aiming at ensuring the efficient and optimised transmission of electricity coming from renewables thanks to superconducting cables.

Power
Voltage
Current
Project duration
Rising amounts of renewable energy coupled with an increase in decentralised power generation call for the modernisation and significant expansion of the European grids.
Superconducting medium-voltage cables could become the preferred solution for energy transmission from renewable generation sites to the electricity grid. Onshore cables can save on size, and offshore cables eliminate the need for costly converter stations required by high voltage DC cables.
The EU project SCARLET (“Superconducting cables for sustainable energy transition”) unites 15 partners from 7 countries around the goal of designing and industrially manufacturing superconducting cables to enable more efficient and less costly power transmission from renewable electricity generation sites. The promise of superconducting cables lies in their high efficiency, compact size, and reduced environmental impact. The SCARLET project will make use of these advantages by developing cables that transfer very high powers in very small conductors.
Learn more about the project:

The project is driven by the concept of exploiting the high current capability of superconducting cables to shift from High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) to Medium-Voltage Direct Current (MVDC) transmission while maintaining comparable power levels. The project aims to develop and industrially manufacture superconducting cable systems at the gigawatt scale, advancing them to the final qualification stage prior to commercialization. The project started in September 2022 and is meant to last four and a half years.
The project will cover the following aspects
- Develop, industrially manufacture, type test and demonstrate full-scale HTS (High-Temperature Superconducting) cables cooled with LN2 for a bipolar 1 GW link (±50 kV/10 kA)
- Design HTS-based offshore superconducting Medium Voltage Direct Current (MVDC) links cooled with LN2 for bipolar 1 GW power transfer (±50 kV/10 kA), and design the offshore cooling system with cooling substations
- Develop, industrially manufacture, type test, and demonstrate full-scale MgB2-based superconducting cables cooled with LH2 for a bipolar 1 GW link (±25 kV/20 kA)
- Design and assess the feasibility of elpipes for multi-GW power transfer
- Define and simulate comprehensive electric system use cases, their protection requirements, and to design and demonstrate a protecting fault current limiter module
- Assess superconducting transmission lines, technically and economically, to identify their beneficial application areas and exploitation paths
More information about superconductivity:
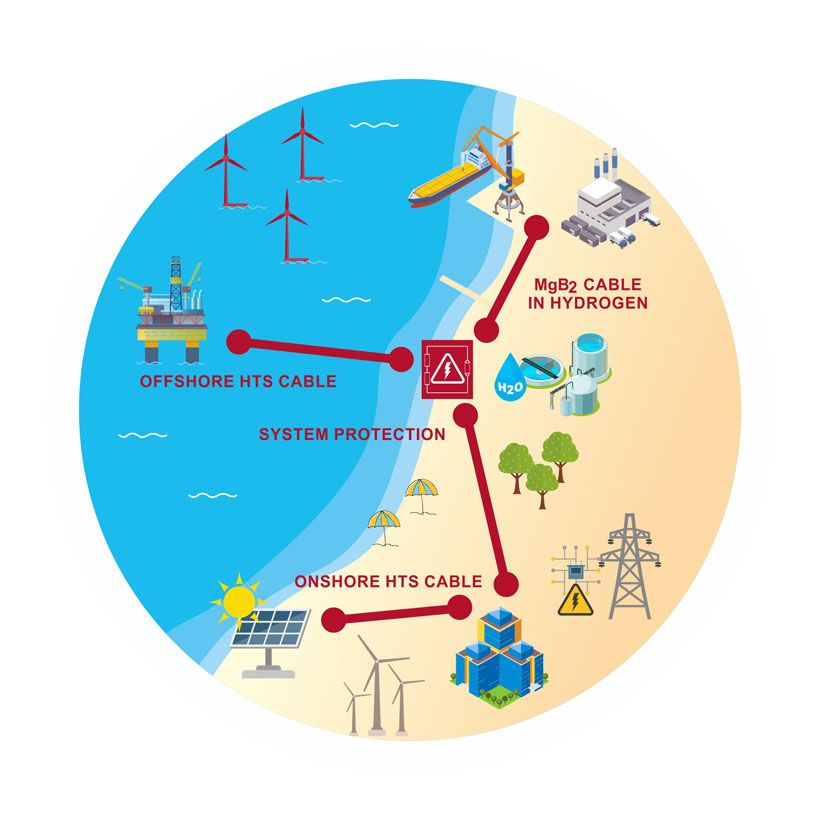
SCARLET aims at developing and demonstrating High-current Direct Current (DC) transmission cables with their auxiliary components, for the renewable sources-based grid, in order to radically decrease costs and losses, and to increase transmission capacity. The consortium partners cover a variety of relevant areas from superconducting research and industry and are grouped around 4 large-scale demonstrators with the following technology-specific objectives:
- Onshore High-Temperature Superconducting (HTS) cable (HTS, 70 K)
- Superconducting cables in liquid hydrogen (MgB2, 20 K)
- System protection
- Offshore High-Temperature Superconducting (HTS) cable
Superconducting cables for sustainable energy transition
Onshore superconducting cable systems are developed and demonstrated, while reinforced cryostats are designed and tested for offshore applications. System protection activities include the development and demonstration of a resistive superconducting fault current limiter (RSFCL) module intended to protect associated switchgear.
In parallel with the demonstrator activities, system architectures are investigated and designed to fully exploit the capabilities of Medium Voltage Direct Current (MVDC) superconducting cables, and techno-economic assessments are conducted.
Both HTS and MgB2-based superconducting cables will be designed for kilometric lengths, and 1 GW cable systems will be brought all the way to the type test, the last qualification step before a commercial installation.
Superconducting medium-voltage cables, based on HTS and MgB2 materials, have the potential to become the preferred solution for energy transmission from many renewable energy sites to the electricity grid.
- Onshore High Temperature Superconducting (HTS) cables provide a compact design, which preserves the environment in protected areas and minimizes land use in urban areas where space is limited.
- Offshore High Temperature Superconducting (HTS) cables compete on cost and – compared to conventional HVDC cables – have the clear benefit of eliminating the need for large and costly converter stations on the offshore platforms. MgB2 cables in combination with safe liquid hydrogen transport directly from renewable energy generation sites to e.g. ports and heavy industries, introduce a new paradigm of two energy vectors used simultaneously in the future.
Both Medium Voltage Direct Current (MVDC) superconducting cables - HTS, cooled with liquid nitrogen, and MgB2, cooled with liquid hydrogen - will be designed, manufactured, and tested, including a six-month test for the MgB2 cable. For grid protection, a high-current superconducting fault current limiter module will be designed and tested. Furthermore, the technology developments will be supported by techno-economic analyses, and a study of elpipes, large cross-section conductors for high-power transfer, will be performed.
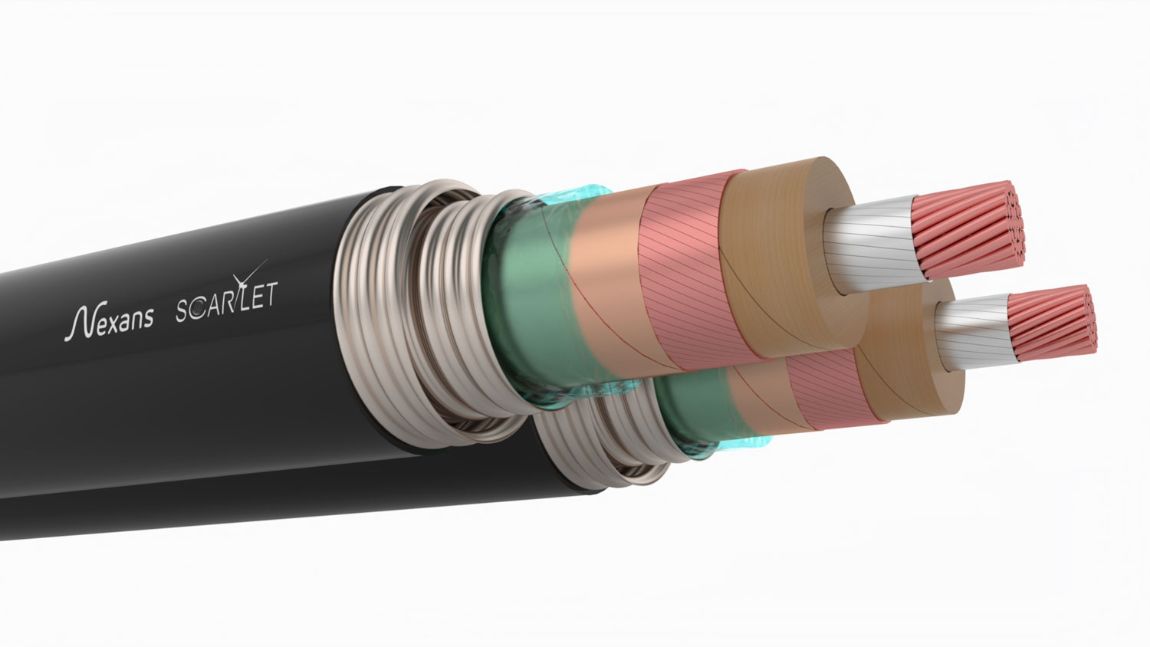
Nexans to design Medium Voltage Direct Current High Temperature Superconducting (MVDC HTS) cable system
Nexans will deliver and test the High Temperature Superconducting (HTS) cable as well as deliver cryogenic envelopes to both the HTS and the MgB2 cables.
Nexans is leading two major work packages in this project
-
Design and modeling of High Temperature Superconducting (HTS) cable systems at 50 kVDC and 10 kA, including manufacturing and testing of the High Temperature Superconducting (HTS) cable prototype at 50 kVDC and 10 kA
-
Design of long-length offshore High Temperature Superconducting (HTS) cable systems at 50 kVDC and 10 kA, including core, cryostat, joints, and shrinkage management. Moreover, to enable long lengths of onshore or offshore High Temperature Superconducting (HTS) cable systems, new sets of accessories have to be developed to allow continuity of the power transmission with cooling systems distributed along the cable route.
Besides designing solutions, the project also contributes to standardization efforts by supporting the integration of Medium Voltage Direct Current (MVDC) superconducting cables into existing frameworks, including the proposal of type test recommendations (testing of Direct Current (DC) superconducting cables as well as certification for the LH2 cryogenic system).
More information about superconducting systems:

Superconductivity to accelerate the Energy transition
Superconductivity is no longer a wishful thinking,it is now a reality. High Temperature Superconducting (HTS) technology offers significant potential for increased efficiency and reduced carbon emissions. The deployment of superconductor technology can facilitate the transition towards a low-carbon society and is poised to contribute significantly to the development of a resilient future power grid.
With more than 30 years of experience, Nexans is the leading innovators in superconducting systems. Our proven track record attests to our advanced engineering expertise and capabilities in High Tempereature Superconducting (HTS) cables and fault current limiters - and clearly demonstrate the technology readiness. So far, superconducting cables have been successfully operated in the electricity grid for several years, for example:
- LIPA project: powering the US grid: Nexans developed and delivered a complete 138 kV Alternative Current (AC) superconducting cable system
- Best Paths: Boosting renewable energy integration: Nexans designed and built a 320 kV Direct Current (DC) superconducting loop including a single 30 m cable carrying a current of 10 kA for a rated power transmission capacity of 3.2 GW.
More information about superconductivity:
Other projects aim at demonstrating how superconductors can also extend the reach of HVAC export cables. The Supramarine consortium is focused on developing this approach. The project will study the electrical connection between offshore wind farms and the coastline using High-Temperature Superconducting (HTS) cables. The objective is to develop a High Voltage Alternating Current (HVAC) superconducting power transmission system demonstrator. Nexans, as the leading innovator in superconducting cables and systems, will ensure the development of the advanced High Voltage Alternative Current (HVAC) superconducting cables, junctions and terminations.
Superconducting grids can facilitate the integration of large-scale renewable energy sources, such as offshore wind farms and remote solar power plants, by giving alternatives to conventional technologies enabling efficient long-distance transmission of bulk power with lower environmental impacts, minimal losses and faster deployment for the full system. This can overcome geographical limitations and unlock the full potential of renewable energy resources.
related news

Our websites
Select your country to find our products and solutions
-
Africa
- Africa
- Ghana
- Ivory Coast
- Morocco
- North West Africa
- Americas
- Asia
- Europe
- Oceania







_reduced.jpg/jcr:content/AmpaCity-(2)_reduced.jpg)
